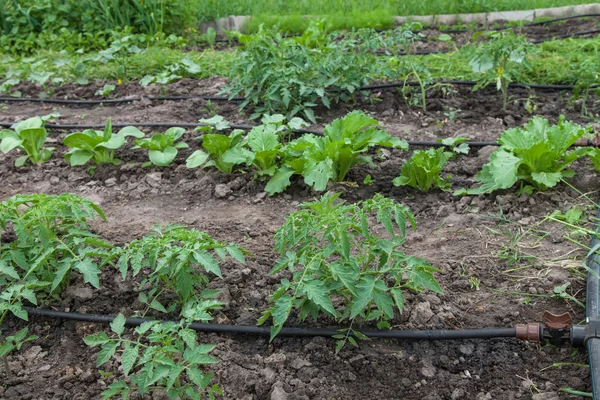
Irrigation is a fundamental practice in the field of market gardening. Water is one of the most important factors for ensuring optimal plant growth and thus obtaining high yields. That is why, for centuries, farmers have sought efficient irrigation systems to guarantee the survival of their crops. In this article, we explore the various innovative irrigation techniques used today to ensure the success of market gardening crops.
Introduction
Irrigation techniques in market gardening have evolved over the centuries, significantly increasing crop yields. However, with growing concerns about water availability, water costs, and the need to reduce the environmental impacts of agricultural practices, farmers are looking for more sustainable and efficient solutions.
In this article, we examine traditional irrigation techniques as well as innovations used today to irrigate market gardening crops. We also discuss water management and technology that allow for optimizing water use to achieve higher yields.
Traditional irrigation systems
Farmers have used traditional irrigation techniques for centuries to irrigate market gardening crops. Among the most common are gravity irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, and flood irrigation.
Gravity irrigation system circulates water in channels that follow the natural slope of the land. The water then slowly flows over the crops, allowing for uniform irrigation. This technique is particularly suitable for flat terrain.
Sprinkler irrigation sprays water on the crops using nozzles. This technique is used on sloping terrain or terrain where gravity irrigation is impossible. It allows for uniform irrigation and can be automated for more efficient water use.
Flood irrigation floods the field with water, allowing for uniform irrigation. This technique is particularly suitable for rice crops, but it can also be used for other crops.
Innovations in irrigation
With growing concerns about water availability, water costs, and the need to reduce the environmental impacts of agricultural practices, many innovations have been developed to irrigate market gardening crops more sustainably and efficiently.
Among the most common innovations are drip irrigation, micro-sprinkler irrigation, and capillary irrigation.
Drip irrigation involves dripping water directly onto plant roots using perforated pipes. This technique allows for more efficient water use by providing water directly to plant roots, thereby reducing evaporation losses.
Micro-sprinkler irrigation involves spraying water on crops using low-flow nozzles. This technique allows for more efficient water use by providing water directly to plant roots, thereby reducing evaporation losses.
Capillary irrigation involves using porous materials to transport water directly to plant roots. This technique allows for more efficient water use by providing water directly to plant roots, thereby reducing evaporation losses.
Water management and technology
Effective water management is crucial for achieving high yields while minimizing water consumption. Several technologies help farmers manage water more efficiently.
Farmers use soil moisture sensors to measure humidity levels and determine when crops need water. Automated irrigation systems then provide water to crops based on the needs identified by soil moisture sensors.
In addition, farmers implement rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store rainwater for later use in crop irrigation. They may also use water treatment systems to purify wastewater and reuse it for irrigation.
By leveraging these technologies, farmers manage water more efficiently, reduce water-related costs, and mitigate the environmental impacts of agricultural practices.
The traditional irrigation system: drip irrigation
Drip irrigation is a traditional irrigation technique that involves controlled water delivery directly to the plant’s roots. This method reduces the amount of water needed while maximizing irrigation efficiency.
Drip irrigation is especially suitable for vegetable crops that require regular and precise watering. This technique reduces water loss through evaporation and also helps limit the development of fungal diseases by avoiding wetting the plant’s leaves.
The downside of drip irrigation is that it can be expensive to set up and maintain, especially for smaller farms.
In France, drip irrigation is a commonly used irrigation system for growing vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and eggplants. This technique is particularly useful in regions with low and irregular rainfall.
In conclusion, drip irrigation is a traditional irrigation technique with many benefits for farmers, gardeners, and green space managers. Although it can be costly to set up and maintain, it saves water and maximizes irrigation efficiency.
Sprinkler irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation sprays water over the entire crop surface, making it particularly suitable for large crops and less permeable soils. It also provides water to plants without wetting them, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. However, this technique can cause significant water loss through evaporation and, under certain conditions, soil erosion.
In France, sprinkler irrigation is commonly used in hot and dry regions, like the South of France, where it supports agricultural production despite challenging climatic conditions. To establish an effective sprinkler irrigation system, careful planning is required to ensure that each plant receives the necessary amount of water. The use of sensors to measure soil moisture and determine the optimal time for watering, as well as the proper positioning of irrigation pipes, contributes to even watering across the crop surface.
However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of sprinkler irrigation. Water can become contaminated with pesticides and fertilizers present in the soil, leading to the pollution of groundwater and surface water. Therefore, adopting sustainable agricultural practices is crucial to minimize the environmental impact of this irrigation technique.
Subsurface irrigation
Subsurface irrigation is a highly efficient irrigation method for greenhouse crops or less permeable soils. It involves using buried pipes to deliver water directly to the plants’ roots. This technique has many advantages, but also some disadvantages.
One of its main benefits is that it reduces water loss through evaporation. Water is delivered directly to the plant roots, avoiding surface water loss. Moreover, this technique helps minimize soil erosion, as water is distributed evenly and gently.
However, it is more expensive to implement than other techniques. Installing buried pipes can be more difficult and costly than installing surface pipes. Additionally, this technique requires regular maintenance to prevent clogging or leakage issues.
Despite these drawbacks, it remains a highly efficient technique for greenhouse crops or less permeable soils. It optimizes water use and minimizes losses, benefiting both the environment and farmers.
French farmers increasingly use this technique in vegetable crops, especially for root vegetables such as carrots, turnips, or potatoes. Aware of the environmental issues related to agriculture, they seek to adopt more sustainable and nature-friendly practices.
Capillary irrigation
Capillary irrigation uses the water supply of plants. Using the surface tension and adhesion forces that hold water in the soil’s interstitial spaces, this method reduces the amount of water needed to irrigate crops. It is particularly suitable for light and sandy soils, where water infiltrates quickly, and other irrigation methods may be less effective. Additionally, capillary irrigation ensures a more even water distribution to roots, reducing plant water stress.
However, capillary irrigation also has disadvantages. Firstly, it can be challenging to control the precise amount of water delivered to plants, which can lead to over-watering or under-watering. Moreover, prolonged use of this technique can promote salt accumulation in the soil, harming plant growth and long-term soil fertility.
Capillary irrigation is an interesting method for light and sandy soils but requires careful management to avoid potential problems such as salt accumulation and control difficulties. Vegetable growers who want to use this technique should carefully study their soil characteristics and adapt their practices accordingly.
Hydroponics and aeroponics: innovative techniques
Innovative hydroponic and aeroponic techniques allow for soilless plant cultivation. In hydroponics, plants grow in a nutrient solution delivered directly to their roots. Aeroponics works similarly, but with roots suspended in the air and receiving the nutrient solution by spraying.
These techniques significantly reduce water and fertilizer needs while producing high yields. However, they can be expensive to set up and maintain.
Water management and technology
Modern water management systems use technologies such as soil moisture sensors, temperature probes, and computer-controlled irrigation systems to optimize water use. These technologies deliver the exact amount of water plants need, maximizing yields and minimizing water loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, irrigation is an essential aspect of vegetable cultivation, and farmers have access to a variety of innovative irrigation techniques to ensure their crops’ success. Traditional techniques such as drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation have proven effective for centuries, while modern techniques like hydroponics and aeroponics offer innovative options for maximizing yields.
Farmers also have access to cutting-edge technologies to optimize water use, maximizing yields while minimizing the environmental impacts of agricultural practices. Ultimately, the key to success in vegetable cultivation lies in the ability to strike a balance between productivity, sustainability, and efficiency.